Water
Seawater
specific heat of water is 4.186 kJ/kgC = 4.186 J/gC
= 1 calorie/gC = 5.375 J/mol·K = 1 Btu/lb-F
specific heat of ice is 2.06 kJ/kgC = 2.06 J/gC
specific heat of steam is 2.1 kJ/kgK = 2.1 J/gK
heat of fusion of ice is 334 kJ/kg = 334 J/g
heat of vaporization of water is 2256 kJ/kg = 2256 J/g
density of fresh water at 20C = 0.998 g/cm³ = 0.998 kg/L
= 998 kg/m³ = 8.33 lb/gal = 62.1 lb/ft³
density of ice at 0C = 0.917 g/cm³ = 917 kg/m³
= 7.64 lb / US gal
speed of sound in water is 1,484 m/s or 3320 MPH
Resistivity of ultra pure water is 182 kΩ·m at 25°C
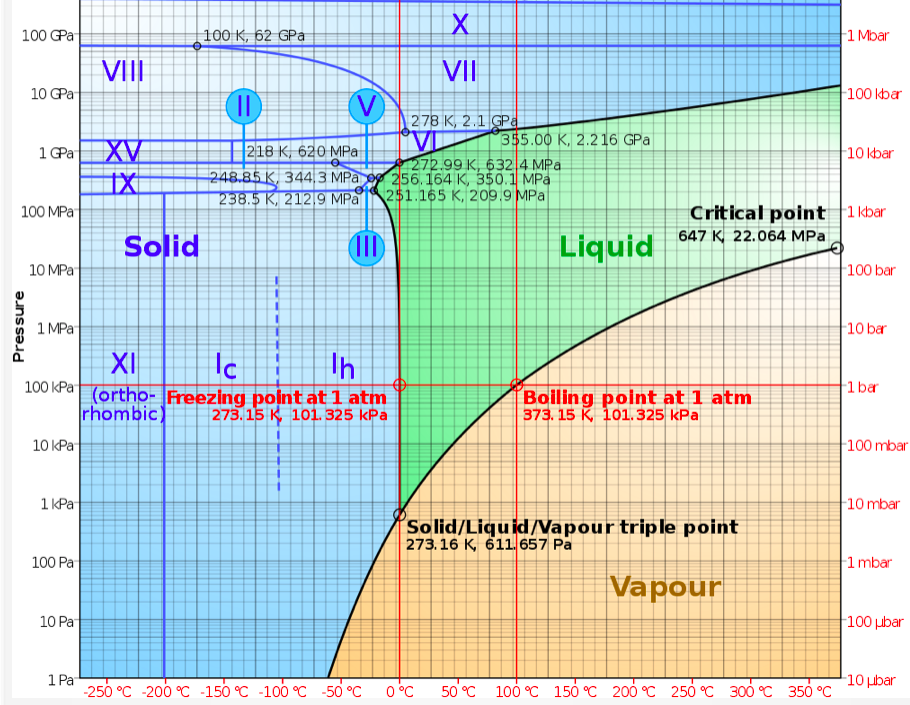
The triple point of water is at a temperature of 273.16K
(0.01 °C) by convention, and at a pressure of 611.73 Pa
Index of refraction
Water (0° C) 1.33346
Water (20° C) 1.33283
Water (100° C) 1.31766
Ice 1.309
The following table list water vapour pressure kPa as a
function of temperature in ºC
T Pressure T Pressure
0 0.6 25 3.2
3 0.8 26 3.4
5 0.9 27 3.6
8 1.1 28 3.8
10 1.2 29 4.0
12 1.4 30 4.2
14 1.6 32 4.8
16 1.8 35 5.6
18 2.1 40 7.4
19 2.2 50 12.3
20 2.3 60 19.9
21 2.5 70 31.2
22 2.6 80 47.3
23 2.8 90 70.1
24 3.0 100 101.3 (1 atmosphere)
specific heat of water versus temperature
10°C 4.1921 kJ/kgC
20°C 4.1818 kJ/kgC
30°C 4.1784 kJ/kgC
40°C 4.1785 kJ/kgC
50°C 4.1806 kJ/kgC
60°C 4.1843 kJ/kgC
70°C 4.1895 kJ/kgC
80°C 4.1963 kJ/kgC
90°C 4.2050 kJ/kgC
100°C 4.2159 kJ/kgC
120º 4.248
140º 4.29
160º 4.35
180º 4.42
200º 4.51
220º 4.63
240º 4.78
260º 4.98
280º 5.29
300º 5.65
325º 6.86
360º 14.6
Density versus temperature
+100°C 958.4 kg/m³
+80°C 971.8 kg/m³
+60°C 983.2 kg/m³
+40°C 992.2 kg/m³
+30°C 995.6502 kg/m³
+25°C 997.0479 kg/m³
+22°C 997.7735 kg/m³
+20°C 998.2071 kg/m³
+15°C 999.1026 kg/m³
+10°C 999.7026 kg/m³
+4°C 999.9720 kg/m³
0°C 999.8395 kg/m³
−10°C 998.117 kg/m³ (super cooled)
−20°C 993.547 kg/m³ (super cooled)
−30°C 983.854 kg/m³ (super cooled)
Density of water versus pressure at 20ºC
1 bar 998.2 kg/m³
25 bar 999.2 kg/m³
50 bar 1000.4 kg/m³
75 bar 1001.5 kg/m³
100 bar 1002.7 kg/m³ Depth of 1020 meters
150 bar 1004.9 kg/m³
200 bar 1007.1 kg/m³ Depth of 2040 meters
(1 bar = 100 kPa)
Density of water versus pressure at 4ºC
1 bar 999.9 kg/m³
25 bar 1001.1 kg/m³
50 bar 1002.3 kg/m³
75 bar 1003.6 kg/m³
100 bar 1004.7 kg/m³ Depth of 1020 meters
150 bar 1007.1 kg/m³
200 bar 1009.4 kg/m³ Depth of 2040 meters
(1 bar = 100 kPa)
Freezing point versus Water pressure.
Pressure Temp.
612 Pa† 0.01ºC (Triple point)
101 kPa 0.0ºC
16.6 MPa –1.25ºC
33 MPa –2.5ºC
60 MPa –5.0ºC
87 MPa –7.5ºC
113 MPa –10.0ºC
138 MPa –12.5ºC
159 MPa –15.0ºC
180 MPa –17.5ºC
200 MPa –20.0ºC
216 MPa –22.1ºC
† Below 611.73 Pa, water does not exist as a liquid
Water Ice versus temperature
Temp density thermal conductivity specific heat
(ºC)(kg/m3) (W/mK)(kJ/kgK)
0 916.2 2.22 2.050 or 0.033 lb/in³, 57.08 lb/ft³
-5 917.5 2.25 2.027
-10 918.9 2.30 2.000
-15 919.4 2.34 1.972
-20 919.4 2.39 1.943
-25 919.6 2.45 1.913
-30 920.0 2.50 1.882
-35 920.4 2.57 1.851
-40 920.8 2.63 1.818
-50 921.6 2.76 1.751
-60 922.4 2.90 1.681
-70 923.3 3.05 1.609
-80 924.1 3.19 1.536
-90 924.9 3.34 1.463
-100 925.7 3.48 1.389
boiling point of water
Clausius–Clapeyron equation
Tb = 1 / ((1/T₀) - (R ln(P/P₀) / ΔH))
T₀ is known boiling point, at P₀
P is new pressure
Tb is new boiling point temperature in K
R is ideal gas constant 8.314 J/Kmol
P is the vapor pressure of the liquid at pressure P
ΔH is the heat of vaporization of the water 40.65 kJ/mol
The boiling point is raised by 0.5 degrees Celsius for
water with 29.2 grams of NaCl dissolved in each kg of water.
Relationship between Liters, m³, cm³, kg for water
1 liter = 0.001 m³ = 0.998 kg at 20C
= 1 liter = 1000 mL = 1000 cm³
100 m³ = 100000 L = 99800 kg
10 m³ = 10000 L = 9980 kg
1 m³ = 1000 L = 998 kg
0.1 m³ = 100 L = 99.8 kg
0.01 m³ = 10 L = 9.98 kg = 9980 g
0.001 m³ = 1 L = 1000 mL = 0.998 kg = 998 g
0.0001 m³ = 0.1 L = 100 mL = 0.0998 kg = 99.8 g
0.00001 m³ = 0.01 L = 10 mL = 0.00998 kg = 9.98 g
0.000001 m³ = 0.001 L = 1 mL = 0.000998 kg = 0.998 g
Seawater at salinity 35 g/kg, which is typical
of the ocean
density of seawater = 1.025 g/cm³ = 1025 kg/m³
= 8.55 lb/gal = 63.8 lb/ft³
Specific Heat at 20ºC 3993 J/KgK
Freezing point −1.910 °C
Boiling point 100.56 °C
thermal conductivity of seawater is 0.6 W/mK
speed of sound in seawater is about 1560 m/s
Added NaCl: For saltwater, the boiling point is raised,
and the melting point is lowered. The melting point is
lowered by 1.85 degrees Celsius if 29.2 grams of salt are dissolved in
each Kg of water (called a "0.5 molal solution" of salt. The Na and Cl
dissociate right away when dissolved, and so for a 0.5 molal solution
of salt, there is a 1.0 molal concentration of ions). The boiling
point is raised by 0.5 degrees Celsius for water with 29.2 grams of
salt dissolved in each kg of water.
Home
Area, Volume
Atomic Mass
Black Body Radiation
Boolean Algebra
Calculus
Capacitor
Center of Mass
Carnot Cycle
Charge
Chemistry
Elements
Reactions
Circuits
Complex numbers
Constants
Curves, lines
deciBell
Density
Electronics
Elements
Flow in fluids
Fourier's Law
Gases
Gravitation
Greek Alphabet
Horizon Distance
Interest
Magnetics
Math
Trig
Math, complex
Maxwell's Eq's
Motion
Newton's Laws
Octal/Hex Codes
Orbital Mechanics
Particles
Parts, Analog IC
Digital IC
Discrete
Pendulum
Planets
Pressure
Prime Numbers
Questions
Radiation
Refraction
Relativistic Motion
Resistance, Resistivity
Rotation
Series
SI (metric) prefixes
Skin Effect
Specific Heat
Springs
Stellar magnitude
Thermal
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal Expansion
Thermodynamics
Trigonometry
Units, Conversions
Vectors
Volume, Area
Water
Wave Motion
Wire, Cu
Al
metric
Young's Modulus